Chronic disease proteome program (CDPP)
„A unique approach combining proteomics and artificial intelligence to enable personalized medicine - reducing organ-damages and loss of life years!"
Who, what, why?
Chronic diseases - the scourge of humanity *
- Chronic diseases lead to permanent restrictions in quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy by up to 20 years!
- Chronic kidney disease increases the risk of cardiovascular disease by up to 20 times.
* UN-Resolution adopted by the General Assembly, 64/265. "Prevention and control of non-communicable diseases", 2011.
They are detected far too late – only when significant organ damage has occurred!
Now: epochal improvement through proteomic analysis
All chronic diseases share pre-existing damage caused by fibrosis and endothelial damage. Even this early damage is now being detected for the first time by proteomic analysis based on collagen proteins in the blood filtrate and urine.

Proteomic analysis combined with artificial intelligence enables the decoding and early detection of chronic diseases
Early detection of chronic kidney disease, heart failure, and coronary heart disease using proteomic analysis alone can reduce the risk of mortality by 30%.
- Diseases arise at the molecular and cellular level, with proteins being the main regulators.
- Drugs usually only act at the protein level and are most effective when used at an early stage of the disease.
Once cells and organs are irreparably damaged, the progressive loss of organ function can no longer be stopped, but at best can be slowed. This is the current situation.
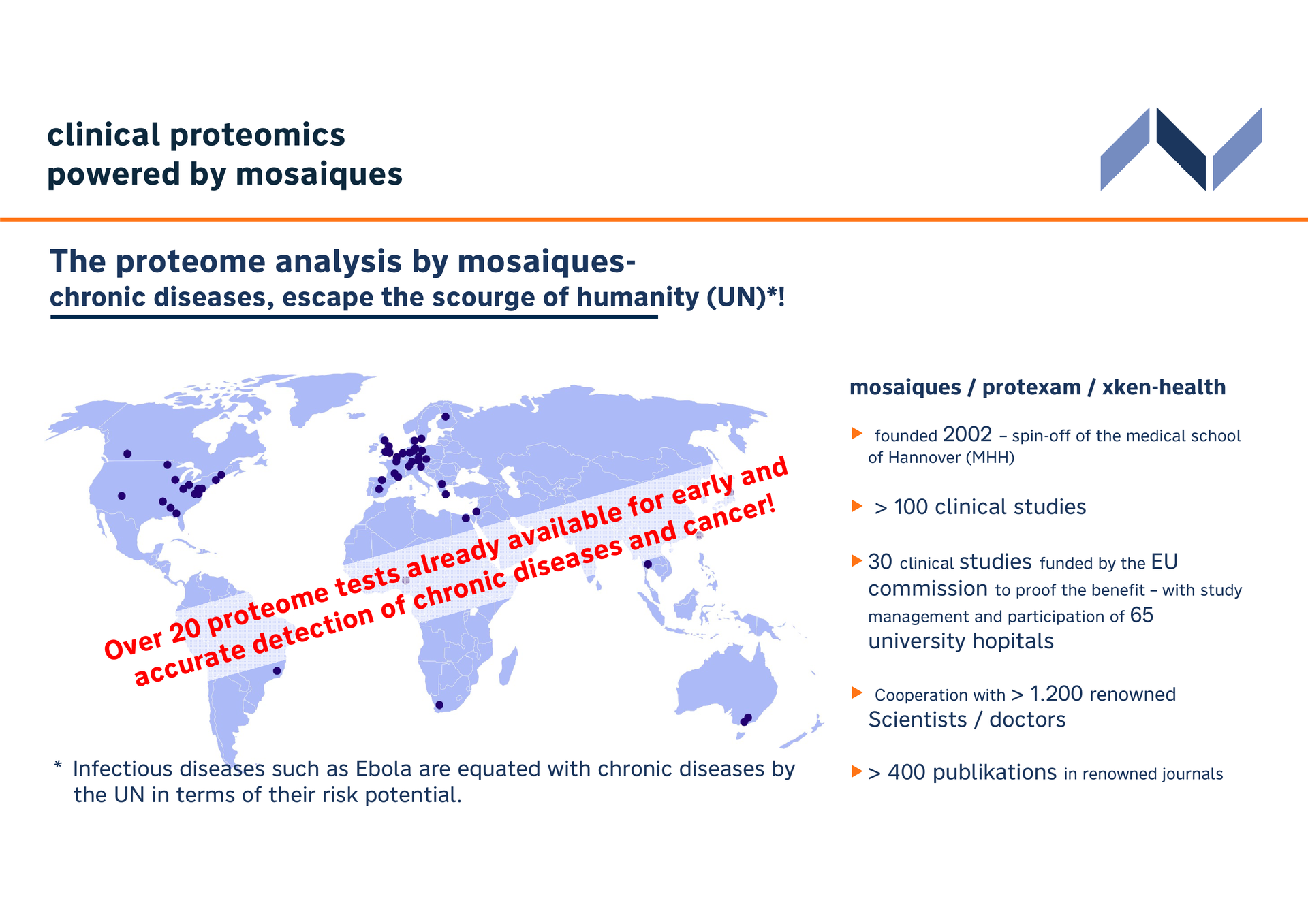
The non-invasive proteomic tests detect chronic diseases early at the molecular and cellular level. The self-learning algorithms, which combine disease-specific protein biomarkers and artificial intelligence, have been validated in over 100 clinical studies. The benefits of the tests, including for cancer, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease, have been described in detail in over 400 scientific publications.
The tests were funded by the EU Commission (among others SYSKID, EU MASCARA, HOMAGE, DC-ren, PRIORITY). The in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tests are registered and approved in the EU.


Further information on clinical proteome analysis and how you can get tested can be found here:
Urine proteome test
The proteome test is highly accurate and can provide reliable information about the development of chronic diseases very early on because, for the first time, the proteome is decoded and extracted from a single sample. All molecular – cellular – disease-specific changes are controlled exclusively by proteins. The primary source for proteome analysis, among many other body fluids, is urine! It is the "filtrate of the blood," extremely stable, for example, compared to blood, which loses much important proteomic information even when frozen at -80° Celsius.
The kidneys are a very delicate organ with approximately 1.7 million filtering units (nephrons) per kidney. They filter approximately 1,700 liters of fluid, essentially "blood," every day (24 hours), and transmit all the proteomic information that has caused the disease-specific changes. The analyzed urine contains up to one million data points and up to 12,000 proteins / peptides.
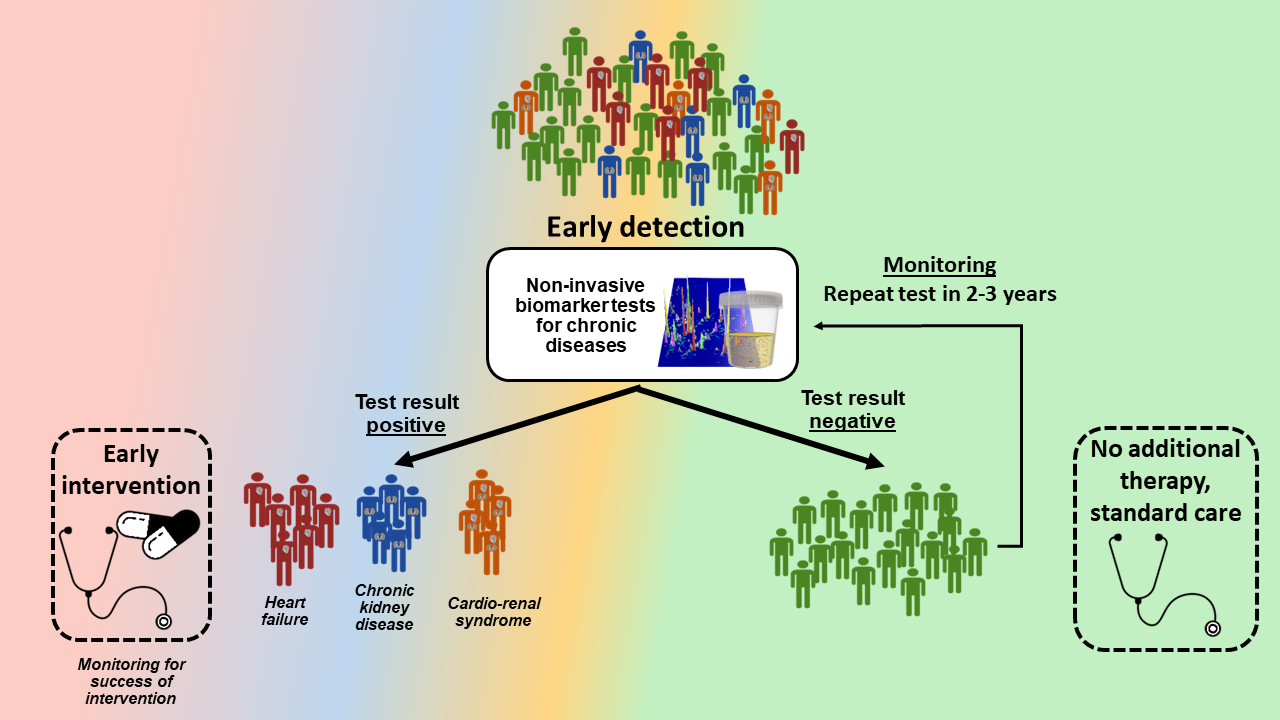
Application and consequences of urine proteomic tests in patients at risk for chronic diseases
In case of a positive test result, treatment, including risk factor management, is initiated according to guidelines to prevent the onset or progression of chronic disease. If urine proteomic testing is negative, follow-up should be performed in 2–3 years.
The unique proteome analysis enables very early and very accurate diagnostics for the first time - here are the study results: